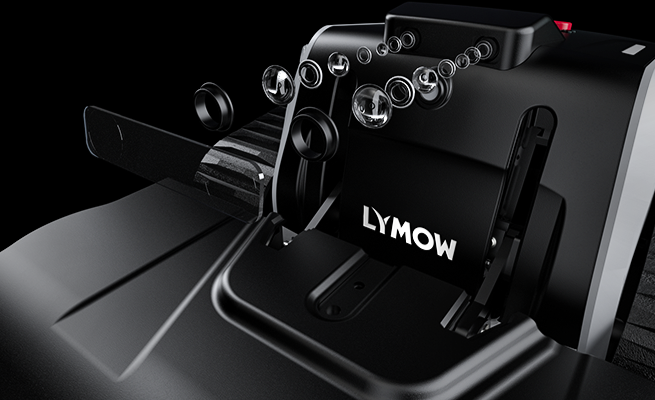
Precision and stability are crucial, and Lymow takes this seriously, ensuring that our lawnmowers deliver dependable performance in all environments.
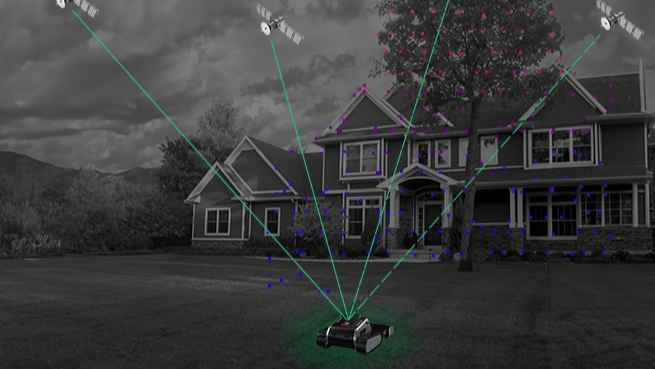
As a user of intelligent lawnmower robots, what are the requirements for robot positioning solutions? There is no doubt that precision and stability are the true product thinking. The stability of all-weather and all-working conditions is the principle that Lymow has always respected and adhered to. Different positioning solutions for lawnmower robots have their own advantages and disadvantages.
For complex lawn conditions, reasonable and reliable sensor solutions and robust and stable positioning algorithm solutions are the real correct choices. The Lymow team has been working hard for this, and the Lymow team is proud to share our thoughts with you.

- Environmental factors
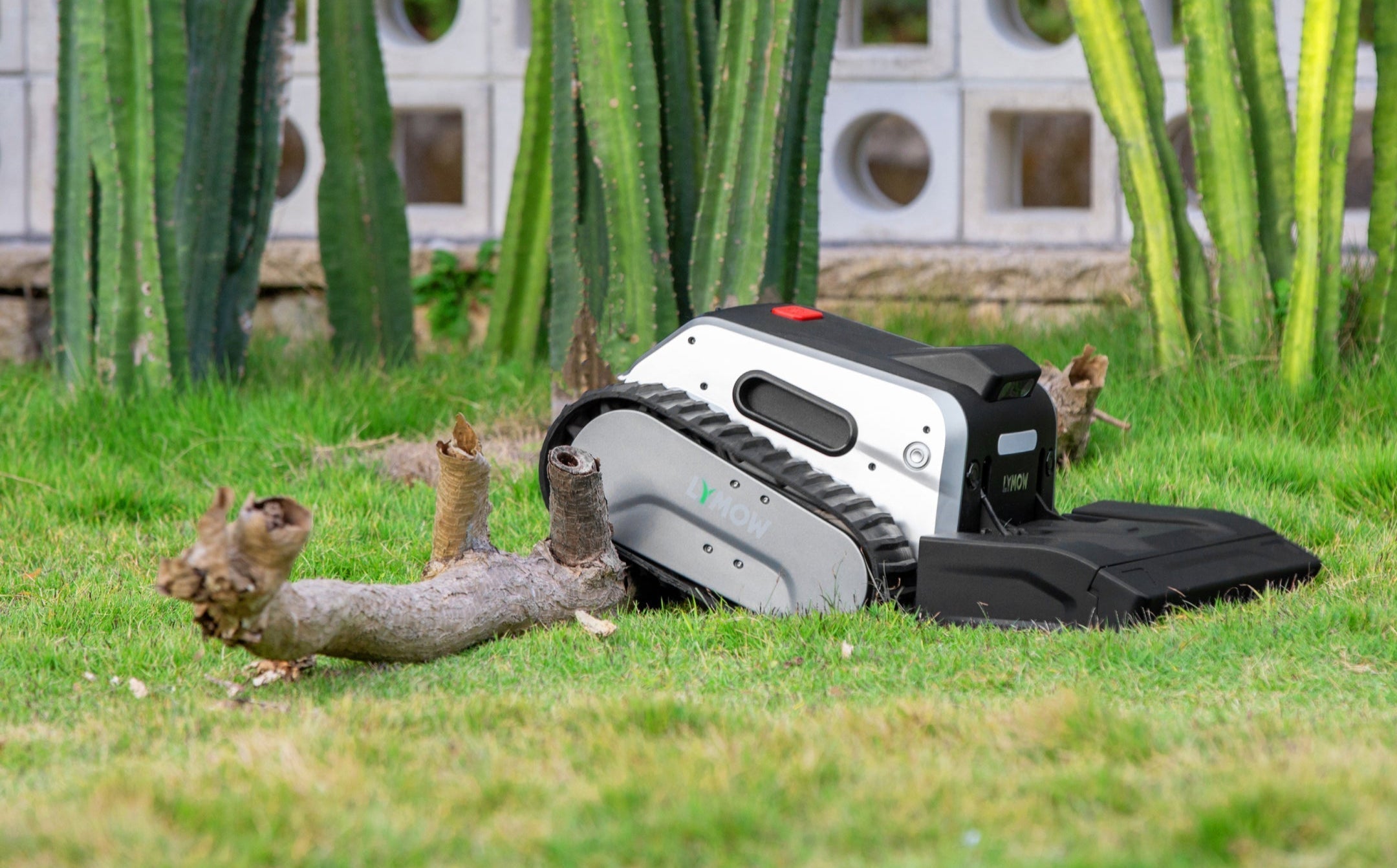
The lawn is not completely flat and may have small mounds, low-lying areas, slopes, etc. When working on slopes, the center of gravity and posture of the lawn mowing robot will constantly change, affecting the measurement accuracy of the sensor and the accuracy of the navigation algorithm, making it difficult to accurately judge its own position and direction of travel. For example, if there is a deviation in positioning during climbing, it may cause the robot to deviate from the scheduled mowing route, and even pose a risk of overturning.
- Vegetation disturbance
Different grass species have different heights, densities, and growth states. Taller or denser grass may affect the sensor's perception of the surrounding environment. For example, the laser beam of a Lidar may be partially blocked by tall grass, making it impossible to accurately obtain distance information of distant objects, affecting the robot's judgment and avoidance of obstacles ahead.
- Effect of lighting conditions
Under strong sunlight, especially on a clear noon, the sunlight may cause glare in the camera, leading to a decrease in image quality and making it difficult for visual sensors to accurately identify key information such as lawn boundaries and obstacles. At the same time, strong sunlight may also interfere with the measurement results of sensors such as Lidar, affecting the accuracy of positioning.
- Weather changes
During rainy days, rainwater can wet the sensors of robots, affecting their performance and measurement accuracy. For example, rainwater may form water droplets on the camera lens, blurring the image. For Lidar, rainwater can refract and scatter the laser beam, affecting the accuracy of measurement results.
- Signal interference
Electromagnetic interference: In some environments, there may be electromagnetic interference generated by other electronic devices or electrical facilities, such as nearby high-voltage lines, wireless communication base stations, etc. These electromagnetic interferences can affect the navigation and positioning signals of lawn mowing robots, leading to sensor data transmission errors or positioning system deviations.
- System itself
There are several mainstream positioning solutions currently available, which will be compared below.
- High-precision positioning: RTK technology can provide high-precision positioning information and achieve centimeter-level positioning.
- Relatively stable: IMU can provide continuous position and attitude information in a short period of time, without being affected by external environmental interference, and can still maintain a certain positioning capability when the satellite signal is temporarily lost.
- The reliance on satellite signals is significant. In environments with obstructions such as buildings and trees, satellite signals may be interfered with, leading to a decrease in positioning accuracy.
- The robustness is poor. When the RTK positioning accuracy is insufficient, the IMU self-sustaining ability is weak, and the system will quickly diverge, which cannot guarantee the continuous stability of the system.
2. Lidar-based positioning scheme
- Lidar can measure the distance information of the surrounding environment by emitting laser beams and receiving reflected signals, and has the characteristics of high accuracy and high resolution.
- It can quickly obtain three-dimensional information of the surrounding environment, which not only helps with positioning but also helps lawn mowing robots avoid obstacles.
- Lidar is not affected by lighting conditions and can work normally during the day and night.
- The high cost and large equipment volume are not conducive to the miniaturization design of lawn mowing robots.
- The laser radar sensor is exposed outside the lawn mowing robot, with a risk of surface damage, and the stains attached seriously affect the system accuracy.
- In environments with dust, fog, etc., the measurement accuracy of Lidar may be affected. At the same time, the detection effect of Lidar is poor for transparent objects and objects with low reflectivity.
- With only ranging information, it is impossible to distinguish the type of obstacle and effectively handle the impact of dynamic obstacles on positioning.
- For high scene requirements, positioning failure occurs in low-structured and open areas; at the same time, sunlight has a great impact on the ranging accuracy of Lidar.
Due to cost, power consumption, and size limitations, the available range of laser radar suitable for lawn mowing robots is mostly only 30-40 meters, which is not suitable for large lawns.
- The cost is relatively low, the power consumption is low, and the sensor stability and lifespan are good.
- Rich visual information can be obtained, and combined with visual perception, the positioning system can fully utilize this information.
- Due to the influence of lighting conditions, the accuracy of visual positioning may decrease in strong or weak light environments.
- Image processing algorithms are complex, technically difficult, and have a high development threshold.
4. Fusion positioning scheme based on RTK + vision
- The integration of multiple positioning technologies can give full play to their respective advantages and improve the accuracy and stability of positioning.
- RTK provides high-precision absolute position information, vision can recognize the characteristics of the surrounding environment, IMU and wheel speedometer can provide continuous posture and motion information, complement each other, and improve the reliability of positioning.
- It has strong adaptability to the environment and can work well in different lighting conditions and terrain environments.
- The system has high complexity, requires complex algorithm fusion and data processing technology, and has a high development threshold.
- The cost is relatively high and requires the installation of multiple sensors.
Based on the above discussion, the Lymow team has always adhered to the technical route of multi-sensor fusion, never wavered, and has achieved good results. We are still working hard, please look forward to our more progress.
Lymow One on Kickstarter:
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/lymowone/lymow-one-boundary-free-robot-mower-for-any-terrain-and-size




30 comments
Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.